Spacecraft: Configuring Planets
Enabling Drag
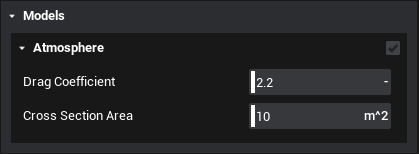
For atmospheric drag to take effect on a spacecraft, both the planet and the spacecraft must have atmospheric drag configured. Create a new spacecraft and place it in a low earth orbit, around 150 km above the surface. In the spacecraft properties tab scroll down to the model's section and enable Atmosphere. Here, the drag coefficient and cross-section area can be defined. The area is not automatically calculated and must be inputted manually.
Planet Information
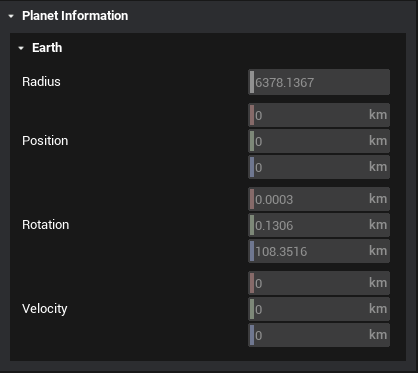
In the planet properties tab, the atmosphere, magnetosphere, and other planet-centric properties can be configured. At the top of this panel, there is some information on the position of the planet in the J2000 frame coordinates.
Configuring Planets
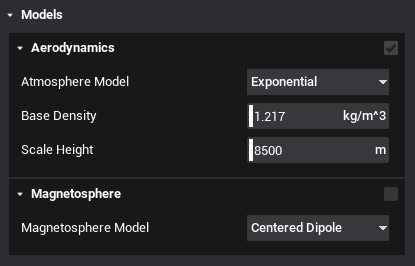
To enable the atmosphere, scroll down to the model section and tick the checkbox on the title bar. Any atmosphere-specific parameters can be specified here but the default values will be valid for the Earth's atmosphere.
Simulating now, the result will have the spacecraft gradually lose altitude. This can happen very slowly and be hard to track in a reasonable time with default values. The magnetosphere can be measured more clearly, however. This can be done by enabling the magnetosphere.
Note
Adding in the atmospheric drag will only work if the atmosphere component on the planet has been enabled. This will be disabled by default.
Adding a Magnetometer
Select one of the spacecraft in the constellation and enter build mode. Add a platform, then append a magnetometer to the spacecraft. This will measure the magnetic field of the Earth. Select the new magnetometer and switch to component properties. A couple of plots can be added to track these values, although this will be covered in more detail in another tutorial. Next to the inventory is another tab called data. In this widget, add a graph. Click on the magnetometer to make sure it is the last thing selected, and then hit Add Property under the plot. Select the SensedNanoTeslas property. Now, start the simulation and witness the sensed values update as the spacecraft orbits the Earth.
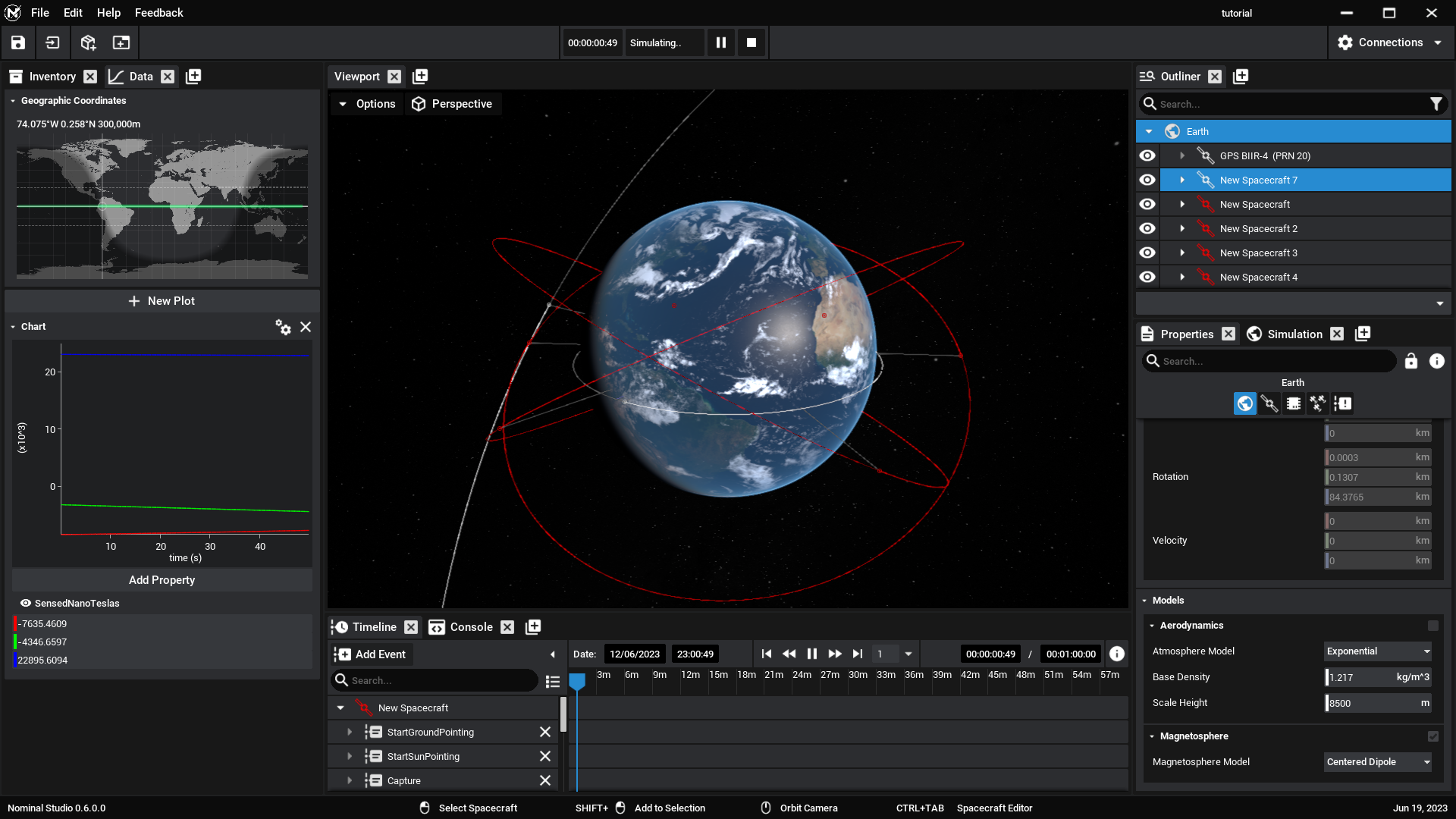
Note
Multiple plots, each with multiple values, can be added to the same graph. These plots can also read data from the database and export it as a CSV file of the data being logged.